Daily intake of vitamins is very important for the proper functioning of the body. However, due to their effectiveness on the most important factors in the human body – the most important include vitamin B12 and folic acid.
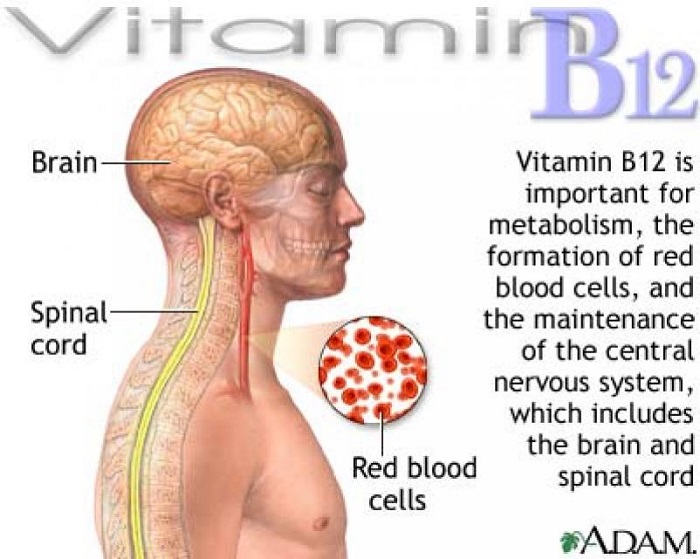
Lack of vitamin B12 in the body can cause many complications, among which the most often is megaloblastic anemia. This very complex and valuable vitamin is indispensable for the normal development of red blood cells, and nerve cells.
Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow, and if formed with a noticeable deficit of vitamin b12, they are of irregular shape and form, many are immature and are not able to perform its most basic function, which is the transport of oxygen to our organs and tissues.
In this article learn where we can find vitamin B12 in food, and how to properly dose it ..
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Symptoms
The first visible symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency are amplified fears or anxiety, concentration problems, hair and skin (eczema, dermatitis, fungal), malaise and fatigue, and unpleasant muscle aches.
However, a larger deficit of this precious vitamin can cause serious nervous disorders, and in the most severe cases – severe damage to the nerves of the spinal cord, leading to paralysis. Vitamin B12 deficiency also causes a heavy degree of anemia, which develops gradually and rather slowly.
The difficulties start with sudden weakness, which is further enhanced by fatigue, heart pounding harder and face becomes pale.
This condition is then accompanied by loss of appetite, bloating, stomach, and a lot of frequent diarrhea stools. This may appear a burning sensation on the tongue, especially when taking some sour foods, and loss of the sense of taste. There are also occurrences of depressive changes, such as memory disorders, paresthesia of extremities, especially the legs, which leads to numbness and tingling.
If the lack of vitamin B12 takes a long time, serious conditions like brain damage and bleeding are also possible. There may even be an increase of the level of homocysteine, which increases the risk of heart attacks and coronary disease.
About 70 percent of people with Alzheimer’s disease had a deficiency of vitamin B12 in the body, so it is very important not to avoid foods that contain it, about which we say more below ..
Vitamin B12 daily dose – DOSAGE
According to its chemical structure, one of the most complex vitamin, and the only one that contains the essential mineral elements and cobalt, is very important for the biological activity. It is crucial for the production of genetic material DNA and RNA, as well as myelin, which provides our protective sheath around the nerves.
Here is how to properly dose vitamin B12 by age in a day ..
- Babies from one to three years -to take 0.9 mcg,
- Younger children aged four to eight years- to take 1.2 mcg
- Children from nine to thirteen– take up to 1.8 mcg,
- Children aged fourteen and older – to 2.4 mcg,
- Pregnant women should consume 2.6 mcg,
- Breastfeeding women should take 2.8 mcg.
- Adults can carry it up to 3 mcg.
Suppose that in our body there is nearly 5mb vitamin b12 (other sources indicate significantly lower quantities of less than 2 mg), provided that during the day one loses about two and a half micrograms.
For clinical deficiency of vitamin B12 in the body, it is considered that it occurs when its overall level drops to about ten percent of normal.
Most of the population through food consumes quite enough of this vitamin, regularly consuming meat, milk, cheese and eggs in the diet, since those are the foods rich in vitamin B12. Another important factor is its correct absorption , and for that, it is primarily necessary that the stomach is completely healthy, as well as the health of the intestinal tract.
Which foods are rich in vitamin B12
The main sources of vitamin B12 are animal products, beef and pork liver, kidneys, heart and muscles, where bacteria produce this vitamin. Eggs and fish are also very good sources, as well as all foods containing lactic acid.
However, this vitamin can also be found in plant foods, but in much smaller amounts. Vegetarians are advised to eat a diet rich in grains, soy products and brewer’s yeast because they can often lack vitamin B12, due to specific plant nutrition.
Also, this vitamin in smaller amounts can be also found in red beet, certain types of grains (especially their germs), sesame, hazelnut, soybeans, seaweed…
Also, a good source of vitamin B12 is sauerkraut, and all foods containing lactic acid, such as pickled vegetables. The recommended daily adult dose is not more than three micrograms.
If you use more, you have no reason to fear and panic, because too much of this vitamin does not cause hypervitaminosis, since B12 is water soluble, so the body does not produce large stocks. In addition, the digestive tract does not absorb it well, so it works in the body with the help of calcium.
If you eat well, the deficit and lack of vitamin b12 will be replaced in the best way possible, without the need for any drug.
Why Is Vitamin B12 So Beneficial
This remarkable vitamin stimulates the formation, growth and maturation of red blood cells- erythrocytes. Like all the vitamins of the B-complex group, it is essential in converting fats, carbohydrates and proteins into energy.
It is great in treating various nerve disorders, has proven antitumor effects, improves your concentration and memory, maintains alertness and reduces irritability and balance, and due to these qualities, it is called the “power vitamin”.
It prevents anemia, promotes growth and increases appetite in children. Vitamin b12 can alleviate discomfort during menstruation and immediately before it. It lowers levels of homocysteine, an amino acid that can damage the walls of arteries and increases the risk of heart disease.
For its complete absorption, one needs to have a completely healthy stomach, and one of its main enemies is helicobacter, which causes infection of mucous membranes, which can lead to ulcers.
Therefore, prevention is extremely important. In the event that you are diagnosed with a deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid, it is best to start adjusting your diet, whereas in the case of more serious deficit you must consult a physician in order to receive the appropriate medical therapy.