There’s no question sweating is beneficial for the body. For one thing, perspiration cools the skin when it’s hot thus protecting you from overheating. Plus, it’s one way the body eliminates toxins.
As useful as it is, sweating, which is typically accompanied by bad odor, can be a great cosmetic issue for most people. It makes you extremely self-conscious and can seriously affect your social life.
Commercial antiperspirants are the most used items to cover the smell and prevent the armpits from sweating.
Interestingly, sweat itself doesn’t stink, but the bacteria thriving in the dark moist places on your body. In fact, sweat from a healthy body is odorless.
Now, the type of bacteria thriving on your body and their particular odor are closely linked to the food you eat and what your body does to eliminate it. In other words, bacteria are largely influenced by their environment. So, when we sweat, bacteria feed on the secret thus releasing a specific smell.
When it comes to its chemical composition, sweat is quite complex. For one thing, it contains excess minerals and metabolic waste including proteins, enzymes, fats, sugars and metals.
Primarily because of the absence of glycerol (a sugar made by the body), adult sweat differs from child sweat. As bacteria thrive on sugar, this is the reason why children don’t normally produce a body odor until puberty.
On the other hand, sweat produced by the feet differs in its chemical composition.
Causes of Body Odor
The number one culprits accountable for bad body odor are foods full of chemical additives, red meats, and processed foods. Also, a number of medications can influence body odor. These include:
Cystagon for kidney disease
Metformin for diabetes
Carnitine for athletic performance
Wellbutrin for depression
Interestingly, body odor can also be triggered by a diet low in carbohydrates as the liver starts using proteins as fuel once it exhausts available carbohydrates. Ammonia, which will be excreted in sweat, is a by-product of protein metabolism.
According to a study, body odor of women is different than body odor of men owing to the way in which fatty acids are processed in the body. Smell, though, both pleasant and unpleasant, differs from person to person.
Some medical conditions will trigger the secretion of an unpleasant odor.
Liver and kidney disease lead to accumulation of toxins in the body resulting in a bleach-like smell.
Diabetes is marked by an over-production of ketones (a type of acid) to compensate for lack of insulin causing a fruity smell.
The following guidelines can help you effectively keep your body odor under control:
Do soak your feet – it’s beneficial, nourishing, and helps your body get rid of bacteria on your skin that cause bad smell.
Do use baking soda – a baking soda paste gently massaged into your armpits is extremely beneficial for cleansing, detoxifying, and eliminating odor. When using this treatment, make sure you wash it thoroughly.
Do take chlorella – this algae is abundant in chlorophyll; it’s great for detoxifying and deodorizing, providing vitamins, minerals, and essential amino acids. Plus, it freshens your breath too.
Don’t use antiperspirant – commercial antiperspirants are laden with harmful chemicals that have repeatedly been linked to breast cancer, headaches, and Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, antiperspirants can even make you smell worse because of the chemical interaction.
Don’t eat processed foods –sugar and chemical additives in processed food cause bacteria to thrive.
Don’t use antibacterial soaps – triclosan, a chemical typically found in antibacterial soaps, kills both good and bad bacteria. Also, it’s an identified endocrine disruptor.
More topical suggestions:
The lauric acid in virgin unrefined coconut oil is a strong antiseptic; plus, this oil is super nutritious and great for the skin health.
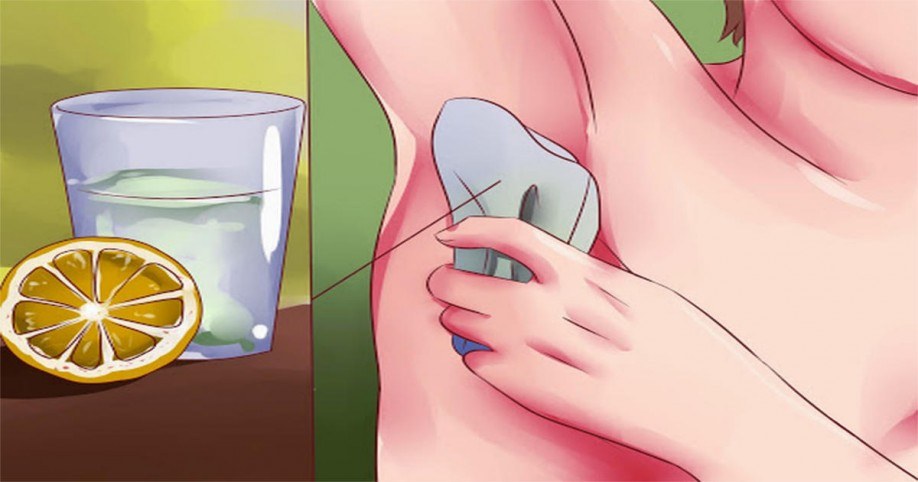
Lemon juice is a powerful natural underarm deodorant because the citric acid it contains kills bacteria. However, make sure you don’t use it immediately after shaving for fear of stinging. Ideally, you should mix it with some water and apply it to underarms. You only need a little to cover the area. It’s also recommended to test for skin sensitivity first.
Diet changes to help reduce toxins and smelly bacteria:
Hydrogenated oils are a big no-no. You should also reduce your consumption of red meat. On the other hand, fiber-rich food, leafy green vegetables, and a lot of tea made from various herbs, such as mint, parsley, oregano, and cilantro, are highly recommended.