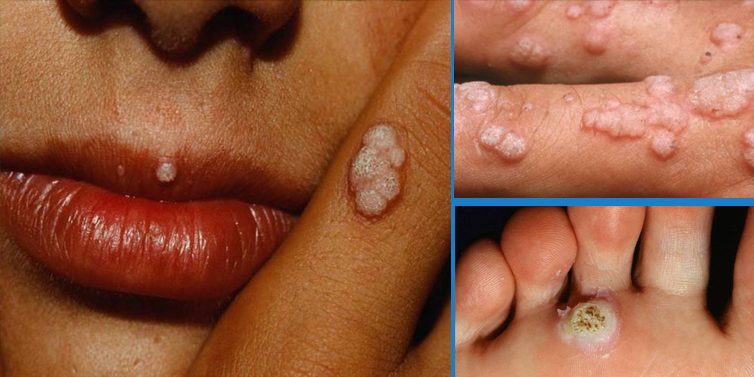
First of all, you should know that this virus is mainly transmitted sexually (ETS), and it affect both women and men. According to the experts, this virus is responsible for cervical cancer, penis, mouth and anus cancer. The human papillomavirus (HPV) is actually a group of viruses that can affect the human skin, and there are over 100 different types of this virus. This is explained in the National Cervical Cancer Coalition of the United States – NCCC. In fact, certain types of HPV cause common warts on the hands and feet. Most types of HPV are harmless, do not cause any symptoms, and go away on their own.
You’ll be shocked when we tell you that almost 40 types of HPV are known as genital HPV as they affect the genital area. The experts warn that up to 80% of females and males will be infected with at least one type of genital HPV at some time. Genital HPV types may be high-risk types that can cause cervical pre-cancer and cancer, or low-risk types that can cause genital warts and usually benign changes in the cervix. This type of virus is easily spread through direct skin to skin contact. Anyone who has any kind of sexual activity involving genital contact could get genital HPV. That means it’s possible to get the virus without having intercourse. And, because many people who have HPV may not show any signs or symptoms, they can transmit the virus without even knowing it. A person can be infected with more than one type of HPV. The medical experts claim that many people get their first type of HPV infection within their first few years of becoming sexually active.
According to the latest statistics, women who are infected with the virus HPV (high-risk), have high chances of developing cervical cancer in the next 10 – 20 years. This is why all women are advised (and women who are no longer sexually active), that they should continue performing their routine gynecologic exams. You should also know that infections in women older than 30 years are less likely to be cured by the body, in natural way. So, they should visit the gynecologist and get a proper treatment.
This is very important for you to remember – the male condoms help reduce the risk of contact. And the female condoms cover more than the male condoms, however, they just reduce the risk of infection. Neither of these two types of condoms eliminate the risk of infection completely. And, you’ll be shocked when we tell you that (according to the latest statistics) almost 30 % of oral carcinomas are HPV-related.
Bottom Line:
- HPV is a common, prolific and highly contagious infection, which is sexually transmitted.
- Condoms cannot provide 100% protection.
- The statistics show that more than 80% of sexually active women will get infected at some time in their lives.
- This virus is mainly transmitted through sexual contact and most people are infected with HPV shortly after the sexual activity.
- This virus can be present, even when the infected individual has no signs or symptoms of the virus.
- In some cases, the symptoms do not appear for years, and are even some cases when people never experience any symptoms during their life.
- It can spread through skin-to-skin contact with infected areas of the skin not covered by the condom such as the male and female genitalia.
- Women are more more “vulnerable” to the virus than men.
- The most common HPV- related disease is cervical cancer. And, you should know that cervical cancer is one of the leading causes of death in women.