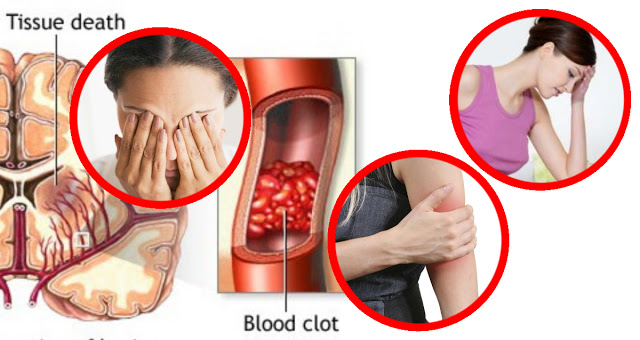
A stroke occurs when an area of the brain is deprived of blood flow or oxygen. The cells in that area of the brain begin to die, and it can affect many different areas of the body. Strokes can come in varying levels of severity, from temporary numbness to paralysis, but all of them need to be treated as an emergency.
Strokes are the third leading cause of death in the United States and the leading cause of long-term disability. Although strokes are more common for those over the age of 65, a quarter of the strokes recorded have occurred in those who were younger. A stroke can happen to anyone, and it is important to know the signs and be prepared. It could mean saving your life or the life of someone you care about.
BE FAST: The Best Way to Recognize a Stroke
There are 5 symptoms that those who are having a stroke will display. If you or a loved one experiences one or more of these symptoms, it is important to get medical assistance quickly. These symptoms are set to the acronym, BE FAST, to help you remember them if you suspect trouble.
B – Balance
Someone who has experienced a stroke will have a sudden loss of balance or coordination. Simple tasks like touching a finger to one’s nose will be impossible. Balance is so severely affected after a stroke that 40% of stroke sufferers will experience a serious fall within the first year following the event.
E – Eyes
Vision will be dramatically affected by a stroke. A person may experience sudden vision changes, double vision, or may even go blind in one eye. About two thirds of those who suffer a stroke will have vision problems; however, vision should improve as the brain repairs itself.
F – Face
Many people will feel numbness in the face, or their face may droop as they are experiencing a stroke. Look for an uneven smile or an eye that appears sleepier than the other.
A – Arm
During a stroke, it is common to feel weakness in an arm. A person will also not be able to raise both arms to equal heights, or may not move one arm at all. Hemiparesis, or weakness in one side of the body, is commonly experienced by survivors of a stroke. They will often have to participate in physical therapy.
S – Speech
If someone is having a stroke, he or she will not be able to speak clearly. Speech will be slurred and difficult to understand. After a stroke, some survivors may even experience aphasia. Aphasia is where the brain is no longer able to understand spoken or written words; it is also difficult for the person with aphasia to choose the correct words for what they are thinking. These issues can only be fixed through speech therapy.
T – Time (Not a Symptom, a Warning!)
Time is critical. If someone is suffering a stroke, call emergency responders right away (911 for the U.S.). If a stroke has occurred, is also important to record when symptoms started and to share this information with medical professionals.
All this information can help a person who is suffering a stroke, but we obviously want to make sure that never happens. Even those who survive a stroke may have to deal with medical problems in the future.