Most of us recognize that unrelenting pain that jolts the inside our skull like lightning, pounds behind the eyes, and reverberates along our temples. Amazing 90 % of people report experiencing the occasional headache, whether it comes in the form of a sharp pain or dull pulsing sensation.
Etiology of Headache
Headaches can result from a wide range of causes both benign and more serious ones. G.Peritz classifies the headache as:
Organic disturbances, caused by cerebral tumors, meningitis, hydrocephalus and syphilis
Functional disturbances, caused by overwork, fatigue, anemia, gout, endocrine irregularities, obesity, intoxications, and reflected pains.
In the first group the pain is not localized, but distributed over the head, sometimes beginning suddenly-with intense severity. It depends on the sudden or gradual (in case of tumors) increase of the intracranial pressure. Sooner or later the signs of intracranial disease become manifest and are diagnosed. This form of headache is often relieved by the lumbar puncture performed for aid in diagnosis.
#1: & #2: Bones and Meninges
The headache of syphilitic origin is of 2 kinds: the one markedly localized in the bones and periosteum, and often the result of irritation of the nerves of the meninges; the other form is indistinguishable from functional headache, and probably also arises from a slight degree of meningitis.
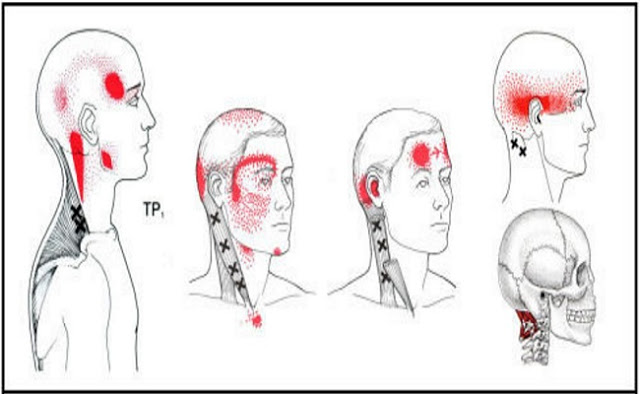
#3: Myalgia – Partial Muscular Contraction
Functional headaches are myalgic and not of cerebral or meningeal origin. Myalgia is a partial muscular contraction,and the degree of pain is inversely proportionate to the resistance of the nervous system. The muscular contraction causes a production of lactic acid, which, if the oxygen supply is insufficient to convert it into glycogen and carbonic acid, is not removed from the muscle and myalgia results.
#4: Headache of Fatigue
Fatigue after walking is due to the excess of lactic acid produced in the muscles. The headache of fatigue and overwork is the result of excessive production of lactic acid in people with poor muscular development.
#5: Anemia
In people with anemia the diminished hemoglobin content of the blood causes deficiency of the supply of oxygen to the muscles, and an accumulation of lactic acid. Similarly, in gouty persons the myalgia is caused by uric acid, the normal removal of which is interfered with ,inciting contraction of the muscular tissues and myalgia.
Modern medicine recognizes 200 different types of headaches depending on their origin.
Headaches hurt, but they do not cause pain to the brain itself. Brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain as it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the pain-sensitive structures around the brain.
Nine areas of the head and neck have these pain-sensitive structures, which are the cranium (the periosteum of the skull), muscles, nerves, blood vessels (that is arteries and veins), subcutaneous tissues, eyes, ears, sinuses and mucous membranes.