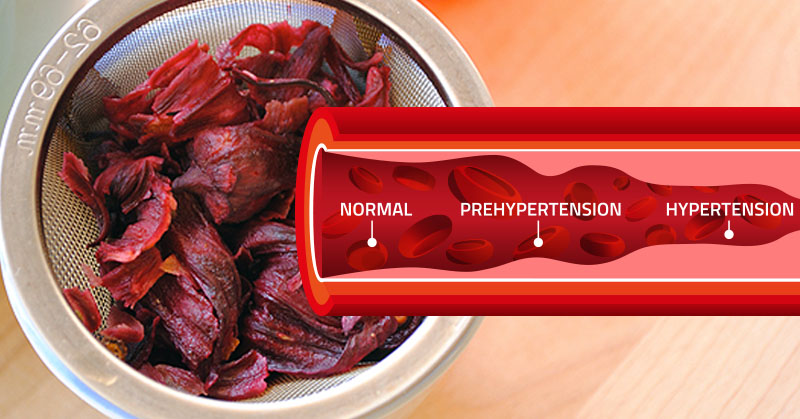
The prevalence of hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is constantly on the rise all across the world. In the U.S alone, it currently affects 70 million adult, which is one in every three adults. It is also worth mentioning that about a third of American citizens have prehypertension, a condition which is characterized by high blood pressure, but not yet HBP. This disease costs the USA $46 billion annually, including the cost of medications, treatment, and health care services.
What is High Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure is a term referring to an increased pressure of blood in the arteries, which may be caused by two major factors:
- The heart pumps blood too forcefully
- The body`s smaller blood vessels became narrow, which causes the blood to exert more pressure
Blood pressure is measured by the amount of force that the heart pumps through the body. The pressure can be measured by the amount of force used, the volume of the pumped blood, and the size and flexibility of the arteries.
Causes of High Blood Pressure
Primary Hypertension is the most prevalent type of HBP. It is believed that genetic factors have a critical role in this condition, including genes that cause abnormalities of the sympathetic nervous system and those affecting blood pressure control.
Secondary Hypertension is typically caused by an underlying medical condition or factors like medications. Among them are:
- Birth defect in the aorta, (the main artery of the heart)
- Endocrine disorders
- Diabetes type 1 and 2
- Kidney disease
- Birth control pills
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including ibuprofen (generic, Advil, Motrin), naproxen (generic, Aleve), and Aspirin
- Corticosteroids
Risk Factors
- Men over 45 and women over 55
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Obesity
- Family history
- Chronic alcohol use
- Chronic stress
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
The Harm in Pharmaceutical Treatment
There are various options for drug treatments for hypertension, including beta blockers, calcium channel blockers (CCBs), diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), and Angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARB). The problem with these drugs is almost all of them cause the patient to feel even worse that the disease itself has caused him to feel in the first place.
Diuretics
Treatment: These drugs help the kidneys flush out excess salt and water in the body and are usually the first treatment prescribed in case of hypertension.
Medication brands:
- Thiazide diuretics – hydrochlorothiazide (HydroDiuril), chlorothiazide (Diuril), chlorthalidone (Thalitone, Clorpres), methyclothiazide (Enduran), indapamide (Lozol), bendroflumethiazide (Naturetin), and metolazone (Zaroxolyn)
- Potassium-sparing diuretics – spironolactone (Aldactone, generic), amiloride (Midamor, generic), and triamterene (Dyrenium, generic)
- Loop diuretics – bumetanide (Bumex, generic), ethacrynic acid (Edecrin, generic), furosemide (Lasix, generic), and torsemide (Demadex, generic)
Complications:
Thiazide diuretics may lower body`s supply of potassium, which in turn increases the risk for heart rhythm disturbances. They are also associated with elevated uric acid levels, erectile dysfunction, and elevated blood sugar levels.
Side effects:
- Urinary incontinence
- Reduced sexual drive
- Fatigue
- Depression and irritability
Beta Blockers
Treatment: Beta blockers slow the heart rate and lower blood pressure levels.
Medication brands: Propranolol (Inderal), acebutolol (Sectral), atenolol (Tenormin), metoprolol (Lopressor), betaxolol (Kerlone), carteolol (Cartrol), nadolol (Corgard), timolol (Blocadren), penbutolol (Levatol), pindolol (Visken), carvedilol (Coreg), and nebivolol (Bystolic).
Complications:
- They may narrow bronchial airways, which makes the drug inappropriate for those with chronic bronchitis, asthma, or emphysema
- They increase the risk for diabetes when combined with a diuretic
- Sudden withdrawals may increase heart rate and blood pressure which can cause angina or a heart attack
Side effects:
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Reduced exercising abilities
- Coldness in extremities (legs, arms, toes, and hands)
- Reduced sexual drive
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Vivid dreams and nightmares
- Depression
- Memory loss
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
Treatment: These drugs widen the blood vessels and reduce the overall workload of the heart, thus treating high blood pressure.
Medication brands: captopril (Capoten, generic), quinapril (Accupril, generic), enalapril (Vasotec, generic), perindopril (Aceon, generic), benazepril (Lotensin, generic), ramipril (Altace, generic), and lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril, generic).
Side effects:
- Irritating cough
- Unfit for pregnancy
- Low blood pressure
Angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs)
Treatment: Just like ACE, ARBs also widen blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
Medication brands: Losartan (Cozaar, Hyzaar, generic), candesartan (Atacand), telmisartan (Micardis), olmesartan (Benicar), valsartan (Diovan), eprosartan (Teveten), irbesartan (Avapro), and azilsartan (Edarbi).
Side effects:
- Raised potassium levels
- Drowsiness
- Low blood pressure
- Nasal congestion
- Dizziness
- Unfit for pregnancy
Calcium-channel blockers (CCBs)
Treatment: CCBs helps relax the blood vessels.
Medication brands: Diltiazem (Cardizem, Dilacor), felodipine (Plendil), amlodipine (Norvasc), isradipine (DynaCirc), nicardipine (Cardene), verapamil (Calan, Isoptin, Verelan), nisoldipine (Sular), and nifedipine (Adalat, Procardia).
Side effects:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Gingivitis
- Rash
- Constipation
- Food interactions
Herbs: The Natural Alternative to Treat High Blood Pressure
1. Hawthorn
This thorny shrub has been long used to treat heart disease. It possesses potent antioxidant flavonoids which improve blood glow, dilate the blood vessels, and protect them from potential damage. The leaves and buds of this herb contain higher amount of flavonoids when compared to the berries. According to a study done on hawthorn, participants who took hawthorn extract for sixteen weeks had lower blood pressure than the placebo.
2. Lime Blossom
The flowers of this herb have been long used to heal issues like anxiety. They contain volatile oil, flavonoids, and mucilage component, all of which work in synergy to soothe inflammation. Interestingly, linden works as potent sedative, diuretic, astringent, and antispasmodic agent.
3. Mistletoe
It has been scientifically shown that mistletoe neutralizes blood sugar levels in diabetics and helps treat cardiovascular disease. It is capable of soothing rheumatic and arthritic pain, too.
4. Hibiscus
In one study male participants aged 30 to 65 years, were given 250 ml of hibiscus tea while the placebo group was given only water. The first group exhibited improvement in blood pressure and inflammation when compared to the placebo volunteers.
5. Yarrow
Yarrow holds a special place in folk medicine in many European countries. It is packed with flavonoids which improve digestion and relax the smooth muscles in the intestine and uterus. Its flowers, stems, and leaves are widely used for medicinal purposes, particularly when it comes to lowering blood pressure and boosting the effects of drugs used for this condition.
Sources:
http://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/facts.htm