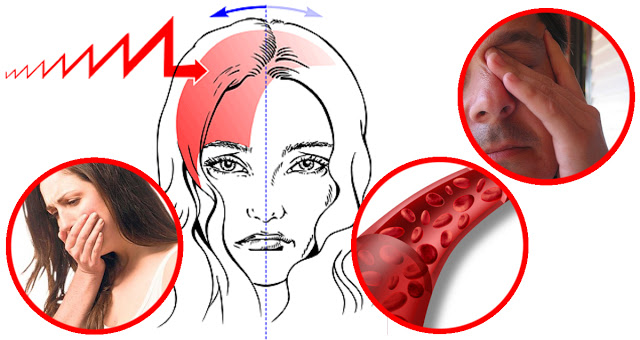
Migraine is a severe headache which is characterized by intense throbbing pain at the front side of the head. It occurs in more than 300 million people worldwide, about 6-7 % in men, and 15-18 % in women. Migraines can last from a couple of hours to three days. On average, there are 20 million migraine attacks occurring every day.
This type of pain is still one of the most difficult to treat and to determine the root cause because there are numerous factors which are known to cause migraine and they vary from person to person.
The common symptoms of migraine include severe, intense and throbbing pain which may occur on one or both sides of the head. Some people experience auras before the attack occurs. People may also experience vomiting, nausea, sweating, sensitivity to light, sound, and smells.
What Causes Migraines?
There are many different theories about the root cause of migraine. Some of them are:
Vascular constriction in the brain
It is caused by blood vessel constriction and decreased blood flow which is followed by dilation of blood vessels, activating the pain-signaling neurons.
Changes in the brain chemical serotonin
Low serotonin levels cause the blood vessels in the brain to become inflamed and swollen, leading to migraine pain.
Excessive increase of blood flow in the brain
There is an opposite theory which claims that migraines are not caused by vasoconstriction and reduced blood flow, but rather by increased blood circulation by 300 percent. However, in certain cases the blood flow may be normal or even slightly reduced when the attack is most intense.