The appropriate sun exposure is the best way to optimize the levels of vitamin D.
However, this sun exposure is limited to 6 months annually, so during the winter, your best choice would be a vitamin D-rich diet, and artificial UVB light, as UV ray exposure has health benefits above and beyond the production of vitamin D.
The UVB exposure from the sun or artificial light produces nitric oxide, which is a compound that lowers blood pressure. On the other hand, standard tanning beds have magnetic ballasts which can emit dangerous EMFs.
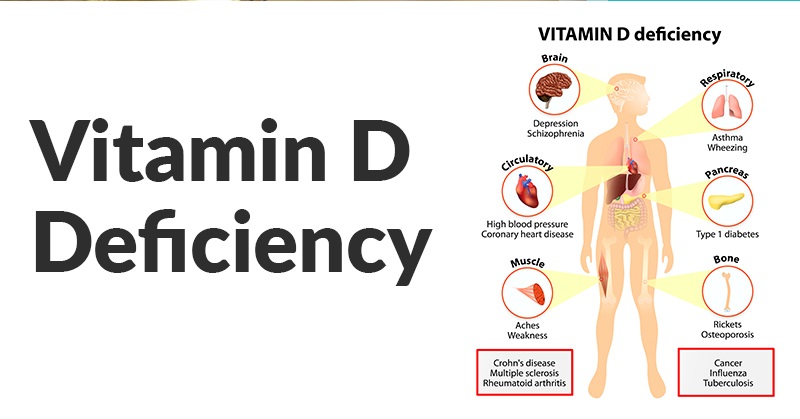
Vitamin D is, in fact, a powerful neuroregulatory steroidal hormone, which provides numerous health benefits. Unfortunately, vitamin D deficiency is a growing epidemic across the world and is the leading cause of numerous health issues.
Therefore, experts claim that if you optimize vitamin D levels, you will reduce the risk of death from any cause by 50%. This is due to the fact that vitamin D influences nearly 3,000of your 24,000 genes, via vitamin D receptors which are located throughout your body.
For instance, vitamin D up-regulates the ability to fight infections and chronic inflammation, and thus protects against flu and colds. It also produces more than 200 anti-microbial peptides, including cathelicidin, which is a naturally occurring broad-spectrum antibiotic.
A January 2013 press release by Orthomolecular Medicine, reported that there is a veritable mountain of research, over 33,800 medical papers, which contain vitamin D in the title or abstract, and indicate that it has powerful beneficial properties for the physical and mental health.
It has been confirmed that vitamin D improves:
- Type 1 and 2 diabetes
- Heart disease and stroke
- Bacterial and viral infections
- Autism, Alzheimer’s, and other brain dysfunction
- Pregnancy outcomes (reduced risk of Cesarean section and pre-eclampsia)
Studies have also found that optimal vitamin D levels treat Crohn’s disease, pain and depression in diabetics, and breast cancer.
Numerous studies have related vitamin D deficiency with the higher risk of Crohn’s disease, but recent studies have shown that there is a “significant interaction between vitamin D levels and Crohn’s disease susceptibility, as well as a significant association between vitamin D levels and genotype.”
Research has found that serum vitamin D levels were significantly lower in patients with Crohn’s disease. Apparently, two out of the 7 DNA sequence variations showed an association with vitamin D levels in those with Crohn’s, and 4 variants were linked to vitamin D levels among controls.
Therefore, vitamin D can affect genetic expression linked to Crohn’s disease.
Moreover, studies have shown that optimal vitamin D levels treat depression and pain in diabetic women. According to PsychCentral:
“The investigators set out to determine how vitamin D supplementation might affect women with type 2 diabetes who were also suffering from depression.
At the beginning of the study, 61 percent of women reported neuropathic pain, such as shooting or burning pain in their legs and feet, and 74 percent had sensory pain, such as numbness and tingling in their hands, fingers, and legs.
During the course of the study, the participants took a 50,000 IU vitamin D2 supplement every week for 6 months. By the end of the study, the women’s depression levels had significantly improved following the supplementation.
Furthermore, participants who suffered from neuropathic and/or sensory pain at the beginning of the study reported that these symptoms decreased at 3 and 6 months following vitamin D2 supplementation.”
The lead researcher Todd Doyle, Ph.D., says that vitamin D supplementation “is a promising treatment for both pain and depression in type 2 diabetes.”
Vitamin D3 and D2
Doctors usually prescribe Drisdol, which is the synthetic form of vitamin D2, made by irradiating fungus and plant matter. On the other hand, D3 is the type produced by the body as a result of the sun or safe tanning bed exposure.
A 2012 meta-analysis by the Cochrane Database, that analyzed mortality rates for people who supplemented their diets with D2 and the ones who did so with D3.
The findings showed that there were huge differences between the two groups. The analysis of 50 randomized controlled trials, which involved 94,000 participants, and found:
- A 6% relative risk reduction among participants who used vitamin D3
- A 2% relative risk increase among participants who used D2
Another study found “a strong additive interaction between abdominal obesity and insufficient 25(OH)D in regard to insulin resistance.”
They discovered that 47 percent of the increased risk of insulin resistance is due to the interaction between insufficient vitamin D levels and a high body mass index (BMI).
Diabetes Care published another study which indicates that vitamin D supplements prevent type 2 diabetes mellitus in people with pre-diabetes.
Apparently, participants with the highest vitamin D levels had a 30 percent reduced risk to develop diabetes during the three-year evaluation period.
Furthermore, a recently featured article in Science World Report shed light on the recommendation by British breast cancer surgeon, Professor Kefah Mokbel, who claims that women should take daily vitamin D supplements to lower the risk of breast cancer.
“Prof. Mokbel has also requested Jeremy Hunt, the Health Secretary, to make [vitamin D] pills freely available as this would result in saving about a 1,000 lives annually. “
He said: ‘I am calling for all women from the age of 20 to be given free vitamin D supplements on the NHS because it is effective in protecting against breast cancer.’
Joan Lappe, professor of nursing and medicine at Creighton University School of Medicine in Omaha, Nebraska maintains:
“…[R]esearch conducted by the Creighton University School of Medicine in Omaha, Nebraska, which analyzed menopausal women from rural eastern Nebraska for over four years, revealed that taking vitamin D supplements along with calcium cut about 60 percent risk of cancer, including breast, lung and colon cancer…’It’s inexpensive, it’s safe, and it’s easy to take. It’s something that should be considered by a lot of people. It’s low-risk with maybe a payoff.”
Researchers have discovered the beneficial effects of vitamin D in the prevention of different cancers, including lung, skin, pancreatic, ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers, and more than 200 epidemiological studies and 2,500 laboratory trials have confirmed these theories.
The American Journal of Preventive Medicine published a study which concluded that a serum 25(OH)D level of more than 33 ng/mL led to a 50 percent lower risk of colorectal cancer.
Also, research published in the International Journal of Cancer confirmed that a mere 10 ng/ml increase in serum vitamin D levels led to a 15 percent reduction in colorectal cancer incidence and 11 percent reduction in breast cancer incidence.
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition published another 2007 study which found that women who received 1,100 IU vitamin D and 1,450 mg calcium daily had a 77% higher risk to survive, after four years of follow up.
Carole Baggerly, the founder of GrassrootsHealth, claims that even 90 percent of ordinary breast cancer may be due to vitamin D deficiency, so breast cancer can be referred to as a “vitamin D deficiency syndrome,” similarly to common colds and seasonal flu.
Optimizing Vitamin D Serum Levels
According to scientists, the bare minimum for cancer prevention is about 40 ng/ml, and the ideal level might be around 60-80 ng/ml.
According to a 2009 review article titled “Vitamin D for Cancer Prevention: Global Perspective,” published in Annals of Epidemiology:
“Higher serum levels of the main circulating form of vitamin D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D), are associated with substantially lower incidence rates of colon, breast, ovarian, renal, pancreatic, aggressive prostate and other cancers. Epidemiological findings combined with newly discovered mechanisms suggest a new model of cancer etiology that accounts for these actions of 25(OH)D and calcium. Its seven phases are disjunction, initiation, natural selection, overgrowth, metastasis, involution, and transition (abbreviated DINOMIT). Vitamin D metabolites prevent disjunction of cells and are beneficial in other phases.
It is projected that raising the minimum year-around serum 25(OH)D level to 40 to 60 ng/mL (100–150 nmol/L) would prevent approximately 58,000 new cases of breast cancer and 49,000 new cases of colorectal cancer each year, and three fourths of deaths from these diseases in the United States and Canada, based on observational studies combined with a randomized trial.
Such intakes also are expected to reduce case-fatality rates of patients who have breast, colorectal, or prostate cancer by half… The time has arrived for nationally coordinated action to substantially increase intake of vitamin D and calcium.”
In general, research by GrassrootsHealth advises adults to take about 8,000 IUs daily to achieve a serum level of 40 ng/ml.
Note that appropriate sun exposure is extremely beneficial, so boost the levels of Vitamin D in this way as much as possible. If you decide to take supplements, note that you should also take vitamin K2.
Member to test your vitamin D levels twice annually, every 6 months and your aim should be to maintain a clinically relevant serum level of 50-70 ng/ml throughout the year.
Test at the highest point, for instance, in August, and in February, at the lowest point.
Since thousands of studies indicate that vitamin D has a vital role in the prevention of diseases, and affects 3,000 genes in the body, you need to do your best and optimize its levels.
In that way, you will successfully prevent and treat the most common diseases of the modern time, and protect yourself from at least 16 different types of cancer, including skin, lung, pancreatic, ovarian, and prostate cancers.
Source: theheartysoul.com